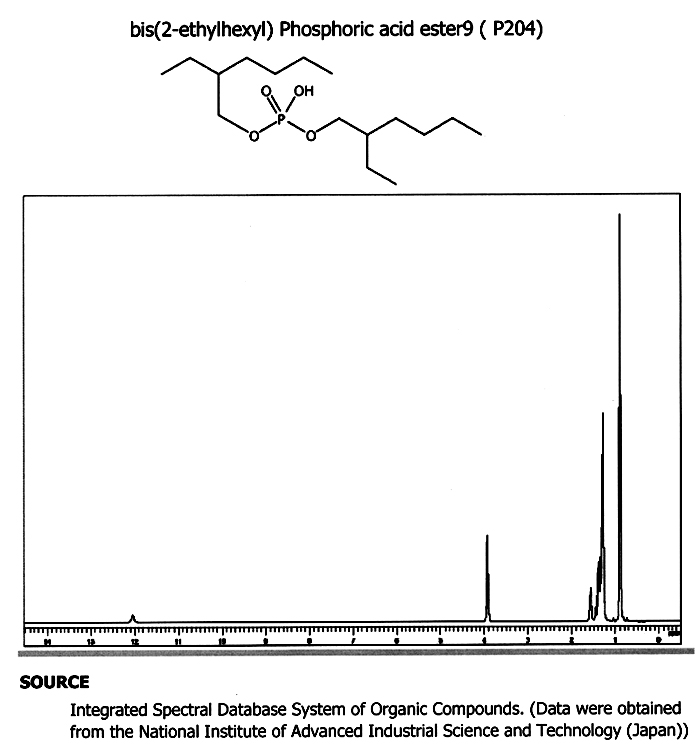
P204 Di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (DEHPA or HDEHP)

CAS: 298-07-7, IUPAC name: Bis(2-ethylhexyl) hydrogen phosphate.
Another CAS No.27215-10-7
IUPAC name: Bis(2-ethylhexyl) hydrogen phosphate
Phosphoric acid,diisooctyl ester;
Isooctanol,hydrogen phosphate (8CI);
Diisooctyl phosphate;
isooctanol, hydrogen phosphate;
Other names:
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phosphate
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) hydrophosphoric acid
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) hydrogen phosphate
BEHPA
BEHP
BEHHPA
BEHHP
Di-(2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid
DEHPA
D2EHPA
Usage:
Di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid (DEHPA or HDEHP) normally be used to remove impurities, then use DZ272 to extract cobalt and magnesium instead of P507, then get nickel from Laterite-Nickel Ore, the efficiency will be raised more than 200 times.
EHPADEHPA is used in the solvent extraction of uranium salts from solutions containing the sulfate, chloride, or perchlorate anions. This extraction is known as the “Dapex procedure.” Reminiscent of the behaviors of carboxylic acids, DEHPA generally exists as a hydrogen-bonded dimer in the non-polar organic solvents.
For practical applications, the solvent, often called a diluent, is typically kerosene. A complex is formed from two equivalents of the conjugate base of DEHPA and one uranyl ion. Complexes of the formula (UO2)2[(O2P(OR)2]4 also form, and at high concentrations of uranium, polymeric complexes may form.
The extractability of Fe3+ is similar as uranium, so it must be reduced to Fe2+ before the extraction.
ITEM |
INDEX |
Appearance |
Colorless, transparent, viscous liquid |
Density (25℃) |
0.973 g/ml |
Chemical formula |
C16H35O4P |
Viscosity (25℃) |
3.47mPa·s |
Flash point |
206°C |
Ignition point |
233°C |
Freezing point |
-60°C |
Boiling point |
209°C (1.33kPa) |
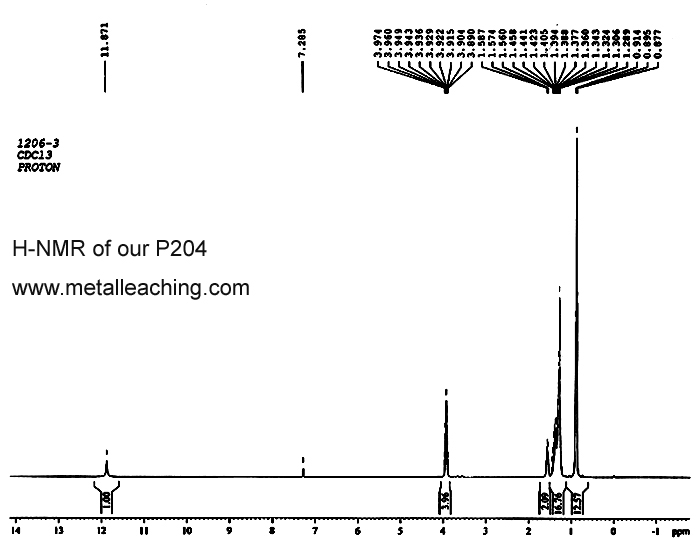
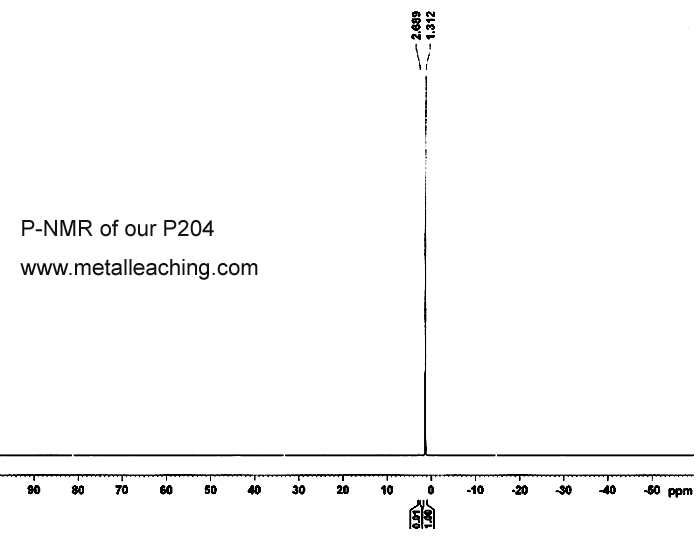
Our P204 is No.1 in China, the quantity is best, appearance is best, content is highest, purity is highest.